About
CCUS Overview
CCUS is Safe
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) recognises CCUS as a safe and effective strategy for achieving net-zero carbon emissions by mid-century. Extensive research and the successful execution of numerous projects globally have demonstrated the technology’s viability and safety when properly managed. With robust monitoring systems and stringent regulatory frameworks in place, CO2 captured through CCUS can be securely stored in geological formations, preventing any leakage into the atmosphere.
Whole of Nation Approach
Ministry of Economy
Steward and integrate CCUS initiatives under one roof by the CCUS Coordination Unit, Environmental and Natural Resources Division, Ministry of Economy, Malaysia.
Federal Ministries and Agencies
State Governments
Civil Society Organisations (CSOs)/Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs)
Academicians
Industry Players
Public
With all the equipment and talent, Malaysia is a country that can offer to trap gas. Hence, a successful bid for CCUS will put the country in a forefront position in the world, in the CCUS industry.”
YB Dato' Seri Rafizi Ramli
Minister of Economy
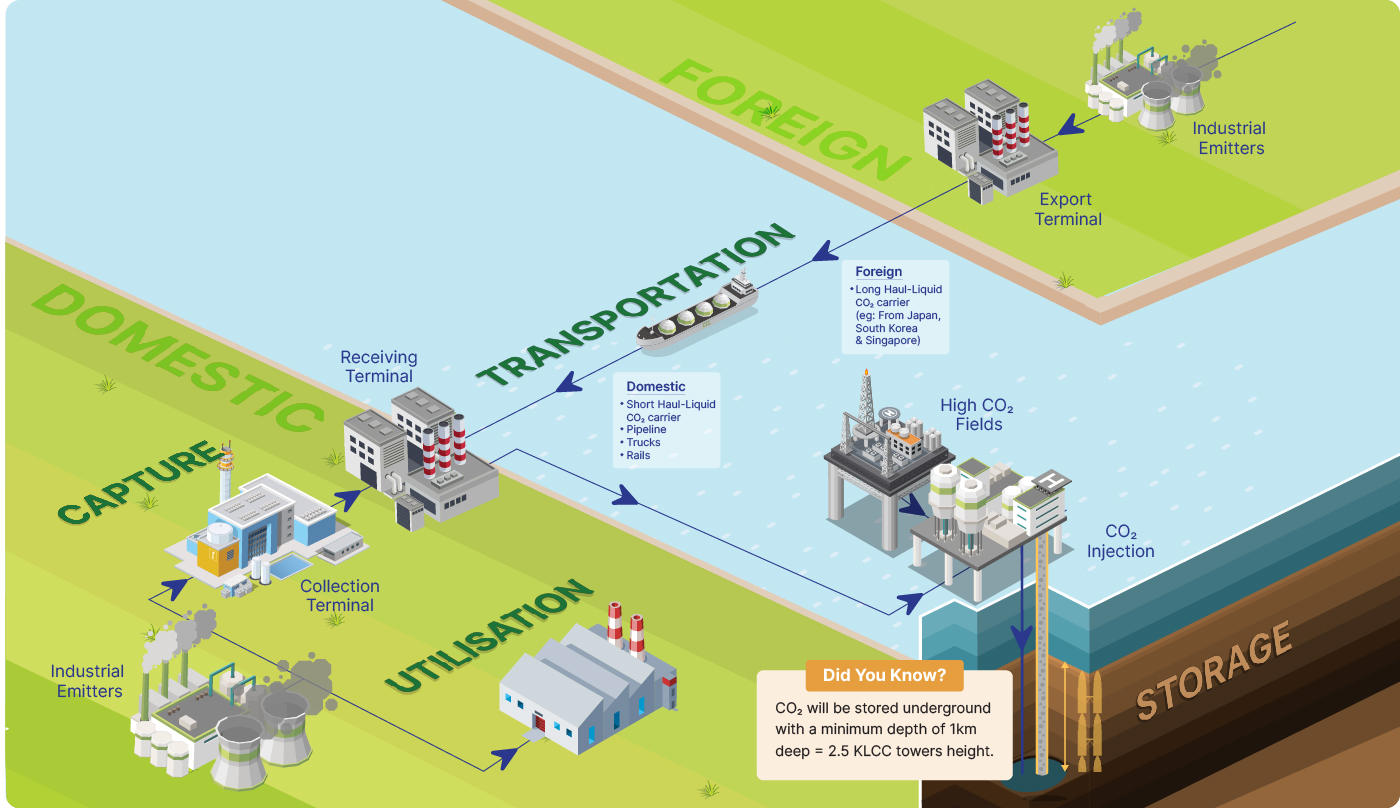
What is CCUS
CCUS stands for Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage. It is a
method to physically remove carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from major industrial sources and the atmosphere, either to be used to produce value added goods or to be stored permanently.
Four main components of CCUS are:
Capturing of CO2
Transportation of CO2
Storage of CO2
Utilisation of CO2
Malaysia’s CCUS Potential
Malaysia views its potential CO2 storage capacity as a valuable resource, not a dumping ground.
With sufficient fields already identified for safe carbon storage, Malaysia is capable of catering to both domestic and regional emissions:
Based on the Global CCS Institute, Malaysia is estimated to possess 13.3 gigatonnes of CO2 storage capacity.
Indicatively, this storage potential surpasses Malaysia's domestic needs, suggesting long-term viability of storage capacity.
Future Uses of Captured CO2
CCUS projects are becoming important link in the transition to new circular economies products such as:
Building Materials
- CO2-cured concrete
- Carbon-negative aggregates
- CO2-based insulation materials
Fuels and Energy
- Synthetic fuels (e-fuels)
- Enhanced geothermal systems
- CO2-based energy storage
Agriculture
- Greenhouse atmosphere enrichment
- Fertiliser production
- Soil amelioration
Environmental Applications
- Water treatment
- pH control in industrial processes
- Algae cultivation for biofuels