What is CCUS?
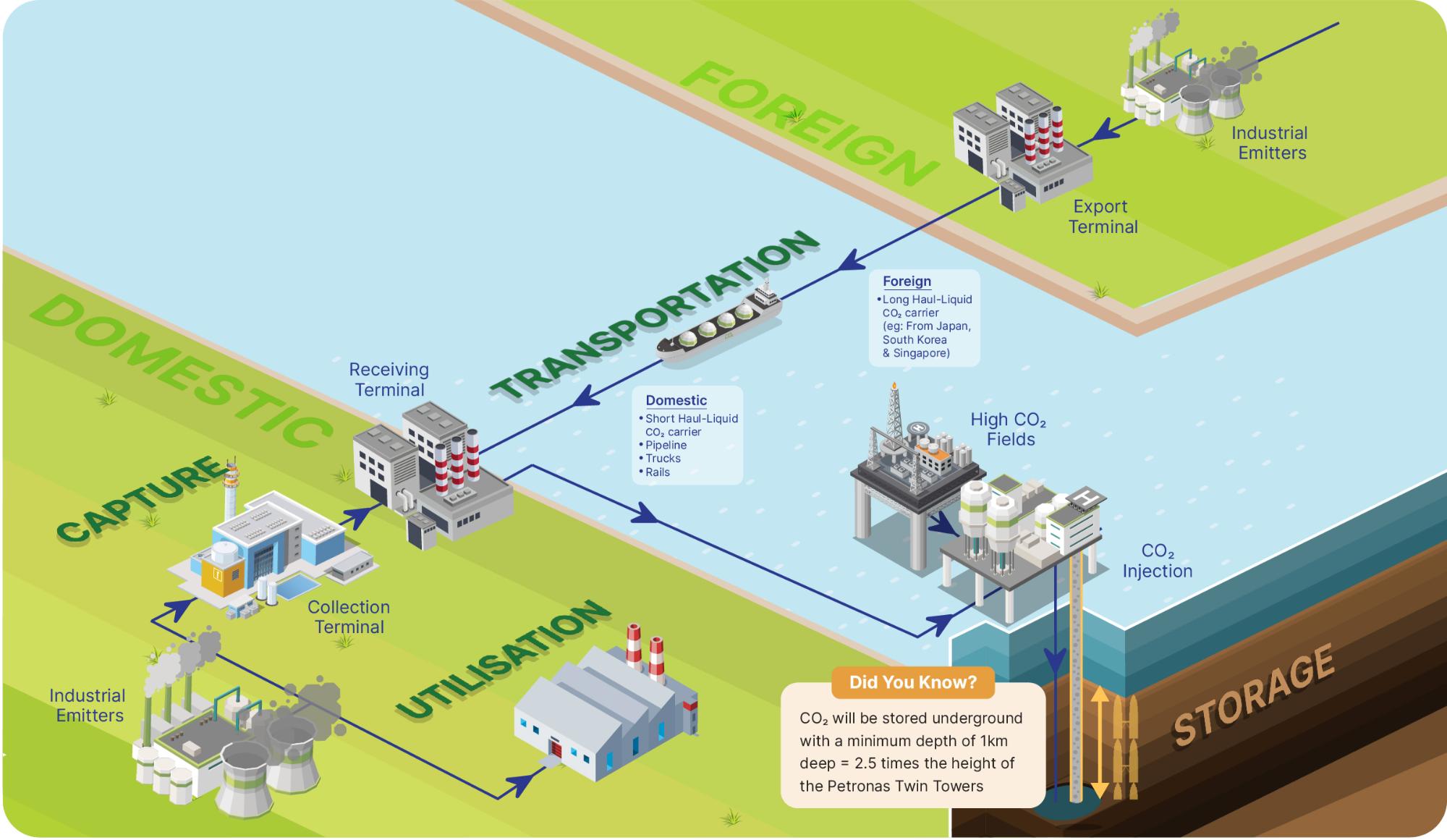
Four main components of CCUS are:
Capturing of CO2
Transportation of CO2
Storage of CO2
Utilisation of CO2
3 Main Methods of Capturing CO2
Method 1
Pre-combustion technology
- Similar to sieving the clumps from the flour before baking
- Excessive CO2 is separated from natural gas before being used to produce electricity or other natural gas products
Method 2
Post-combustion technology
- Works like a giant air purifier for factories and power plants
- Catches CO2 after fuel is burned, before it escapes into the air
- Can be added to existing facilities like fitting a filter to an exhaust pipe
Method 3
Oxy-fuel
combustion
- Burns fuel with pure oxygen instead of regular air
- Generates emissions primarily composed of CO2 and water vapour.
- Makes it easy to separate and capture CO2
- Akin to having a dedicated playroom that is easier to clean up
Future Uses of Captured CO2
Building Materials
- CO2-cured concrete
- Carbon-negative aggregates
- CO2-based insulation materials
Fuels and Energy
- Synthetic fuels (e-fuels)
- Enhanced geothermal systems
- CO2-based energy storage
Agriculture
- Greenhouse atmosphere enrichment
- Fertiliser production
- Soil amelioration
Environmental Applications
- Water treatment
- pH control in industrial processes
- Algae cultivation for biofuels
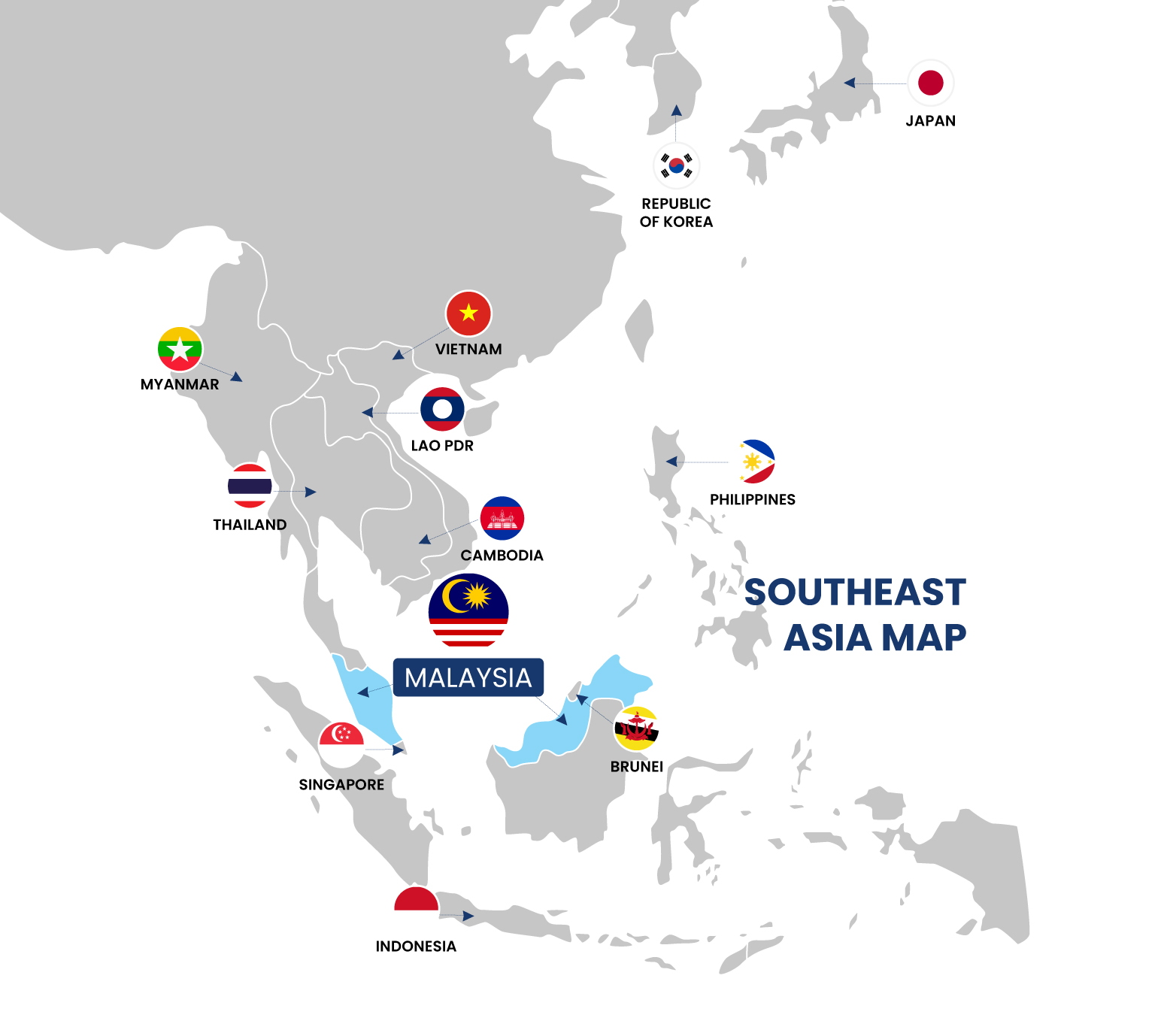
Establishing Malaysia as A Regional Hub
Establishing Malaysia as A Regional Hub
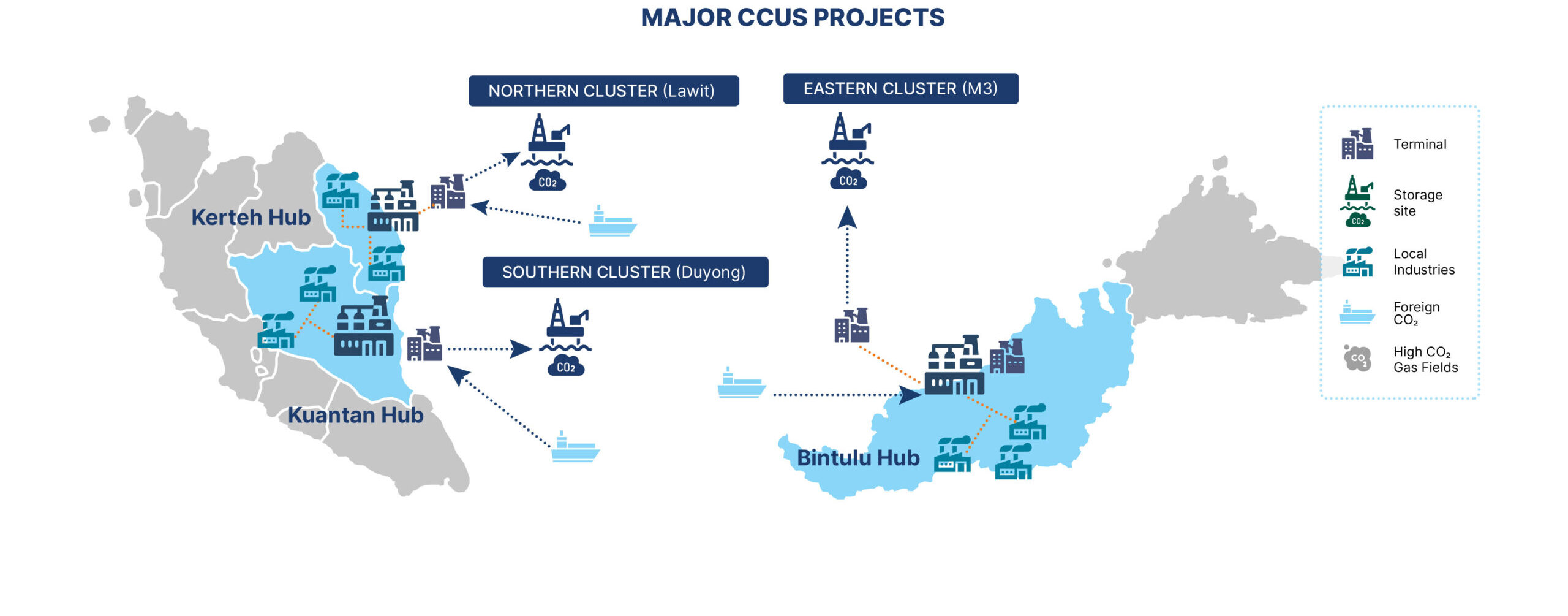
Major CCUS Hubs in Malaysia
Malaysia’s CCUS Potential
Based on the Global CCS Institute, Malaysia is estimated to possess 13.3 gigatonnes of CO2 storage capacity.
Indicatively, this storage potential surpasses Malaysia's domestic needs, suggesting long-term viability of storage capacity.
9 Key Messages
CCUS Initiative Is Safe
CCUS Is Needed To Help Malaysia Achieve Net Zero Aspiration By 2050
CCUS Reduces the Impact of Climate Change
Managing CCUS Risk Through the Development of Comprehensive Legislation and Regulations and Effective Governance of CCUS Activities in Malaysia
There are 5 risks identified including environmental degradation and CO2 leakage at storage sites that can be addressed by a robust and wholesome legislation and standards.
CCUS Helps Local Hard To Abate Sectors To Address CO2 Emissions
CCUS Reduces Decarbonisation Costs for Local Hard To Abate Sectors
Malaysia Has the Potential to Become a CCUS Regional Hub
CCUS Drives New Industry Growth
CCUS Increases Malaysia's GDP
CCUS Empowering Economic Benefits
for Malaysia
CCUS Empowering Economic Benefits for Malaysia
GVA
200-250
billion USD
New Job
Creation
200,000
cumulative per year
CCUS Initiatives
Transforming emissions into opportunities

Steel Manufacturing
Cement Admixture

Petrochemical Feedstock

Steel Manufacturing
Cement Admixture

Petrochemical Feedstock
E-Fuel
Generation
E-Fuel Generation
Fertiliser and
Agricultural Production
Oil and Gas Operations
Moments

Dewan Negara lulus RUU CCUS 2025
Image Source: utusanborneo.com Published by Utusan Borneo (25 March 2025). For more details, read the full news coverage here: Dewan

RUU CCUS perkukuh NETR dan ekonomi hijau negara
Image Source: tvsarawak.my Published by tvsarawak (25 March 2025). For more details, read the full news coverage here: RUU CCUS